All You Need to Know About Generator Transfer Switches: A Complete Guide
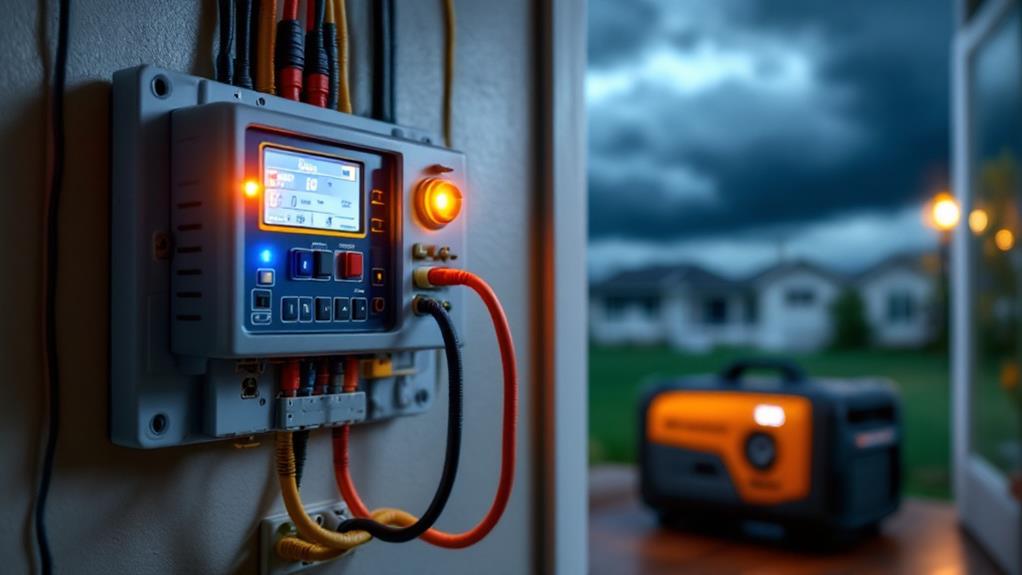

A generator transfer switch is a vital safety device that connects your backup power system to your home's electrical panel. It guarantees smooth transitions between utility and generator power during outages, preventing dangerous backfeeding. You'll find two main types: automatic switches that detect outages and engage the generator, and manual switches requiring you to flip a lever. When choosing a transfer switch, consider your power needs, electrical service capacity, and generator output. Appropriate sizing and installation by a licensed electrician are essential for safety and functionality. By understanding transfer switches, you'll be well-equipped to keep your home powered during emergencies.
What Is a Transfer Switch?
In the world of backup power systems, a transfer switch plays an essential role. It's the device that safely connects your generator to your home's electrical system, ensuring a seamless changeover between utility power and backup power during an outage. A transfer switch prevents backfeeding, which can be dangerous to utility workers and damage your equipment.
There are two main types of transfer switches: manual and automatic. Manual transfer switches require you to physically flip a switch to change power sources. They're typically less expensive but require your presence to operate. Automatic transfer switches, on the other hand, detect power loss and switch to generator power without any intervention. They offer convenience and peace of mind, especially if you're away from home during an outage.
Transfer switches come in various sizes to match your generator's output and your home's electrical needs. They can be installed indoors or outdoors, depending on your setup. When choosing a transfer switch, consider factors like your generator's capacity, the circuits you want to power, and whether you prefer manual transfer operations or automatic transfer capabilities. Proper installation by a licensed electrician is essential for safety and compliance with local codes.
Types of Transfer Switches
When it comes to transfer switches, you'll encounter several distinct types, each designed to meet specific needs and applications. The two main categories are automatic transfer switches (ATS) and manual transfer switches (MTS).
Automatic transfer switches are the more sophisticated option. They'll detect power outages instantly and switch to your generator power without any intervention. This seamless swap guarantees minimal downtime, making ATS ideal for critical applications like hospitals, data centers, or homes where continuous power is essential. They're typically more expensive but offer convenience and reliability.
Manual transfer switches, on the other hand, require you to physically flip a switch to change power sources. While they're less convenient, they're often more affordable and simpler to install. MTS are suitable for less critical applications or situations where you don't mind manually overseeing the power transfer.
Within these categories, you'll find further variations. Some transfer switches are designed for specific voltages or amperage, while others cater to single-phase or three-phase power systems. There are also hybrid models that combine features of both automatic and manual switches, offering flexibility in operation.
How Transfer Switches Work
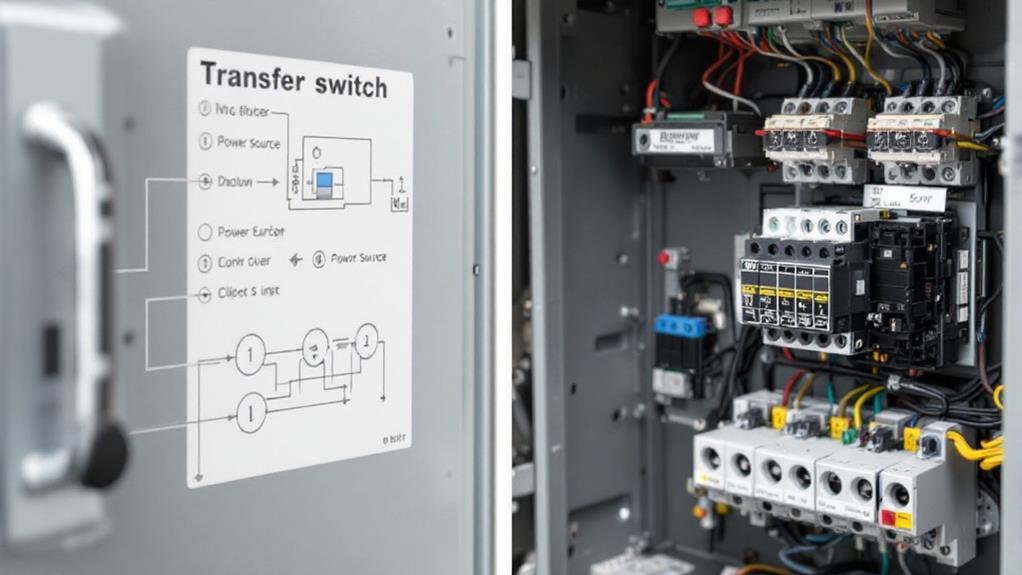

Transfer switches kick into action during power outages, serving as the critical link between your main power supply and backup generator. These devices monitor your home's electrical system constantly, detecting any interruptions in the main power supply.
In manual operation, you'll need to physically flip the switch to move from utility power to your generator. This requires you to be present and alert during an outage. You'll also need to switch back once utility power is restored.
Automatic operation, on the other hand, seamlessly handles the shift without your intervention. When a power loss is detected, the switch signals your generator to start up. Once the generator is running at full capacity, the switch transfers the electrical load from the utility to the generator. When main power returns, the switch detects this and reverses the process, shutting down your generator after a cool-down period.
Both types of switches use a series of contactors or relays to make and break electrical connections. They're designed to prevent backfeeding, ensuring your generator doesn't send power back into the grid, which can be dangerous for utility workers.
Benefits of Transfer Switches
Understanding how transfer switches operate lays the groundwork for appreciating their numerous benefits. When you install a transfer switch, you're investing in a safer and more reliable power system for your home or business.
One of the primary advantages is efficient energy management. Transfer switches allow you to seamlessly move between utility power and your generator, ensuring you're always using the most appropriate energy source. This not only optimizes your power consumption but also extends the life of your generator by preventing unnecessary use.
You'll experience reduced power interruptions with a transfer switch in place. During outages, the switch automatically activates your generator, minimizing downtime and protecting sensitive electronics from sudden power loss. This is especially important for businesses that rely on continuous operations or homeowners with medical equipment.
Transfer switches also enhance safety by eliminating the need for extension cords running from your generator. This reduces trip hazards and the risk of electrical fires. Additionally, they prevent backfeeding, which can be dangerous for utility workers trying to restore power.
Sizing Your Transfer Switch
Choosing the right size for your transfer switch boils down to understanding your power needs. You'll need to take into account your home's power load capacity and electrical service requirements to guarantee you select a transfer switch that can handle your generator's output and your household's demands.
To properly size your transfer switch:
- Calculate your total power requirements by adding up the wattage of all appliances and devices you want to run during an outage.
- Determine your home's electrical service capacity, typically 100, 200, or 400 amps.
- Choose a transfer switch that matches or exceeds your calculated power needs and electrical service capacity.
Installation Process and Considerations
Once you've selected the right transfer switch, it's time to focus on installation. The process requires careful planning and attention to electrical requirements. First, determine the ideal location for your transfer switch, typically near your main electrical panel. Guarantee there's enough space for safe operation and maintenance.
Before beginning, check local regulations and obtain necessary permits. Many jurisdictions have specific permit considerations for generator installations. It's indispensable to comply with these to avoid legal issues and ensure safety.
Next, shut off the main power supply to your home. Install a new circuit breaker in your main panel to connect the transfer switch. Mount the transfer switch securely, following manufacturer instructions. Connect the appropriate wires from your main panel to the transfer switch, ensuring proper color coding and secure connections.
Wire the generator inlet box to the transfer switch, then connect your chosen circuits to the transfer switch. Label all circuits clearly for easy identification during power outages. Finally, test the system thoroughly to verify proper operation.
For your safety and to meet electrical requirements, it's highly recommended to hire a licensed electrician for this installation.
Safety Features and Regulations

Safety is paramount when it comes to generator transfer switches. These devices are designed with multiple safety features to protect you, your property, and utility workers. When choosing and installing a transfer switch, you must adhere to electrical safety guidelines and guarantee fire code compliance.
Key safety features of generator transfer switches include:
- Interlocking mechanisms that prevent backfeeding electricity into utility lines
- Overload protection to safeguard against excessive current draw
- Grounding systems to minimize the risk of electrical shock
You'll need to familiarize yourself with local regulations and national standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), to confirm your installation meets all safety requirements. Many jurisdictions require permits and inspections for transfer switch installations, so check with your local building department before starting the project.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and effective troubleshooting are critical for keeping your generator transfer switch in ideal condition. To guarantee optimal performance, you should conduct regular inspections of your transfer switch, checking for signs of wear, loose connections, or corrosion. Clean the unit periodically, removing any dust or debris that may have accumulated.
Performance monitoring is essential for identifying potential issues before they become major problems. Keep an eye on the switch's operation during scheduled testing, noting any unusual sounds, delays, or incomplete transfers. If you notice any irregularities, consult the manufacturer's manual or contact a professional technician.
Common troubleshooting issues include failure to transfer, incomplete transfers, or delays in switching. These problems may stem from low battery voltage, faulty relays, or damaged wiring. If you're comfortable with basic electrical work, you can check these components yourself. However, for complex issues or if you're unsure, it's best to call a qualified electrician.
Remember to keep detailed records of all maintenance activities and any problems encountered. This information can be priceless for diagnosing recurring issues and planning preventive maintenance. By staying proactive with your transfer switch's upkeep, you'll ensure its dependability when you need it most.
Cost Factors and Budgeting

When it comes to generator transfer switches, understanding the cost factors and budgeting appropriately is essential for making an informed decision. The purchase price of a transfer switch can vary greatly depending on its type, capacity, and features. Manual switches are generally less expensive than automatic ones, but they require more hands-on operation. You'll also need to consider the installation costs, which can add substantially to the overall expense.
Operating costs are another pivotal factor to consider when budgeting for a generator transfer switch. These include:
- Fuel consumption for the generator
- Regular maintenance and servicing
- Potential repairs or part replacements
To ensure you're budgeting accurately, obtain quotes from multiple suppliers and installers. Don't forget to factor in any necessary electrical upgrades to your home or business. It's also wise to ponder the long-term value of your investment. While a more expensive automatic transfer switch may have a higher upfront cost, it could save you money and hassle in the long run through increased reliability and convenience. By carefully weighing these cost factors, you'll be better equipped to make a sound financial decision for your generator transfer switch needs.
Choosing the Right Transfer Switch
Now that you've considered the financial aspects, it's time to focus on selecting the appropriate transfer switch for your needs. When choosing a transfer switch, you'll need to evaluate several factors to guarantee optimal performance and safety.
First, determine the amperage rating required for your electrical system. This should match or exceed your main electrical panel's rating. Next, decide between a manual or automatic transfer switch. Manual switches are more affordable but require physical intervention, while automatic switches offer convenience and faster response times during outages.
Consider the number of circuits you want to power during an outage. Some transfer switches allow for selective circuit coverage, improving energy efficiency and electrical load balancing. Look for switches with built-in surge protection to safeguard your appliances and electronics.
Evaluate the transfer switch's compatibility with your generator and electrical system. Make sure it meets local building codes and regulations. Pay attention to the switch's weather resistance if it'll be installed outdoors. Lastly, contemplate future expansion needs when selecting your transfer switch to avoid costly upgrades later on.



