How Are Houses Connected to the Power Grid? A Complete Guide

You're connected to the power grid through a series of crucial processes. It starts with electricity generation at power plants using diverse energy sources. High-voltage transmission lines then carry this electricity over long distances. Substations play a critical role by transforming high voltages to safer, lower levels for consumption. The electricity travels through the distribution network, further reduced in voltage by transformers suited for home use. Ultimately, it enters your home via a service drop connected to the breaker panel. Your home's wiring guarantees safe appliance operation. Want to understand each step in detail and how it maintains reliability?
Power Generation Process
Electricity springs to life at power plants, where diverse energy sources are harnessed to generate power. You've got a variety of options contributing to this process, including renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power. These sources play a significant role in ensuring energy efficiency and reducing carbon footprints. As power generation progresses, maintaining grid stability becomes fundamental. This involves balancing supply and demand, which smart technology helps achieve by optimizing energy flow and minimizing waste.
Energy storage systems, like batteries, are crucial in this process. They store excess energy generated during peak production and release it when demand is high, smoothing out fluctuations and ensuring a consistent supply. This not only improves grid stability but also boosts overall energy efficiency. Smart technology further aids in monitoring and controlling the power generation process, making it more responsive and adaptive to changing conditions.
Transmission Lines Overview
As electricity makes its passage from power plants to your home, transmission lines play an imperative role in this process. They're responsible for carrying high-voltage electricity over long distances, guaranteeing that power generated at the plant reaches urban and rural areas alike. Understanding the different transmission types is vital, as they dictate how efficiently and safely electricity travels.
Transmission lines come in two main types: overhead and underground. Overhead lines are the most common, supported by tall towers and visible above ground. They're cost-effective and easier to maintain, but they can be vulnerable to weather conditions. Underground lines, on the other hand, are less susceptible to weather but are more expensive to install and repair.
Voltage levels are another significant factor in the transmission process. High voltage levels, often ranging from 69 kV to 765 kV, are used to reduce energy loss during the transmission over long distances. By utilizing higher voltages, electricity can travel more efficiently, reaching your local distribution network with minimal loss.
Role of Substations
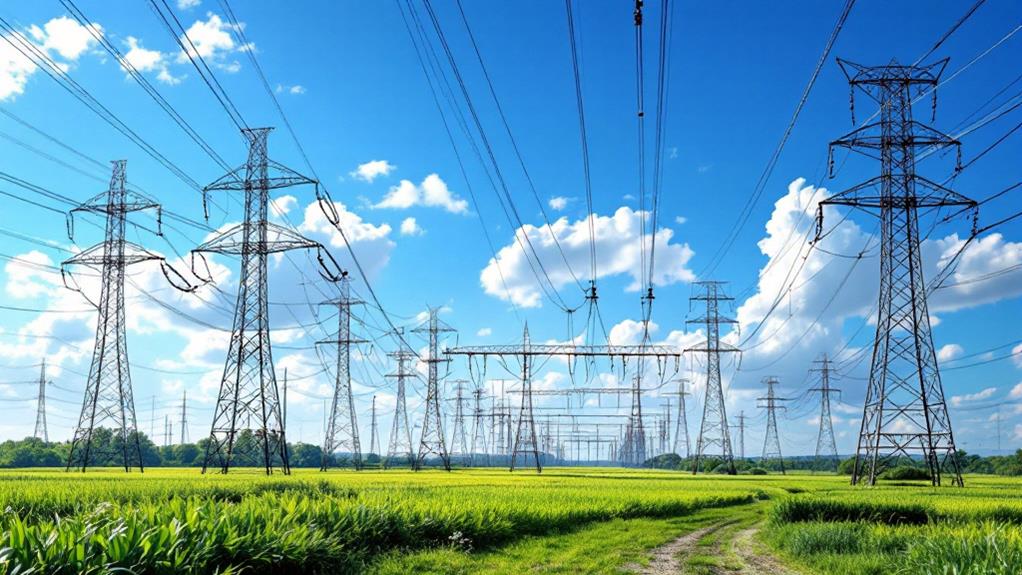

After electricity travels those long distances via transmission lines, it reaches substations, which play a vital role in the power grid. Substations act as gateways that transform high-voltage electricity from transmission lines into lower voltage suitable for distribution to homes. You can think of substations as the middlemen that guarantee electricity safely and efficiently makes its way to your neighborhood.
Understanding substation functions is fundamental. They perform several key tasks:
- Voltage Transformation: Substations reduce the high voltage from transmission lines to a level that can be safely used in homes.
- Switching Operations: They manage the flow of electricity by switching circuits on and off, helping to route power where it's needed most.
- Power Monitoring: Substations track electricity flow, securing consistent and reliable power delivery.
The substation equipment needed to perform these functions includes transformers, circuit breakers, and control systems. Transformers handle voltage changes, while circuit breakers protect the system by interrupting power during faults. Control systems monitor operations and guarantee everything runs smoothly. By performing these tasks, substations maintain the balance and reliability of the power grid, making certain your home receives the electricity it needs.
Distribution Network Explained
Once electricity is stepped down to a lower voltage at the substation, it enters the distribution network, the final stage in delivering power to your home. The distribution infrastructure consists of power lines, transformers, and substations that work together to guarantee electricity reaches you efficiently. These components are strategically placed to maintain grid reliability, so you can enjoy uninterrupted power.
In the distribution network, electricity travels through overhead or underground power lines. Overhead lines are more common in rural areas, while underground lines are typically found in urban settings. Both methods have their pros and cons, but they're designed to keep electricity flowing smoothly.
Transformers play a vital role in this network by further reducing the voltage to levels suitable for residential use. This guarantees that when electricity reaches your neighborhood, it's at a safe and usable voltage.
Distribution infrastructure is fundamental for grid reliability, guaranteeing a consistent power supply despite weather conditions or demand fluctuations. Utilities constantly monitor and maintain this network to prevent outages and keep the power grid functioning efficiently. By understanding this system, you can appreciate the complexity behind the simple act of flipping a switch in your home.
Home Electrical Connection
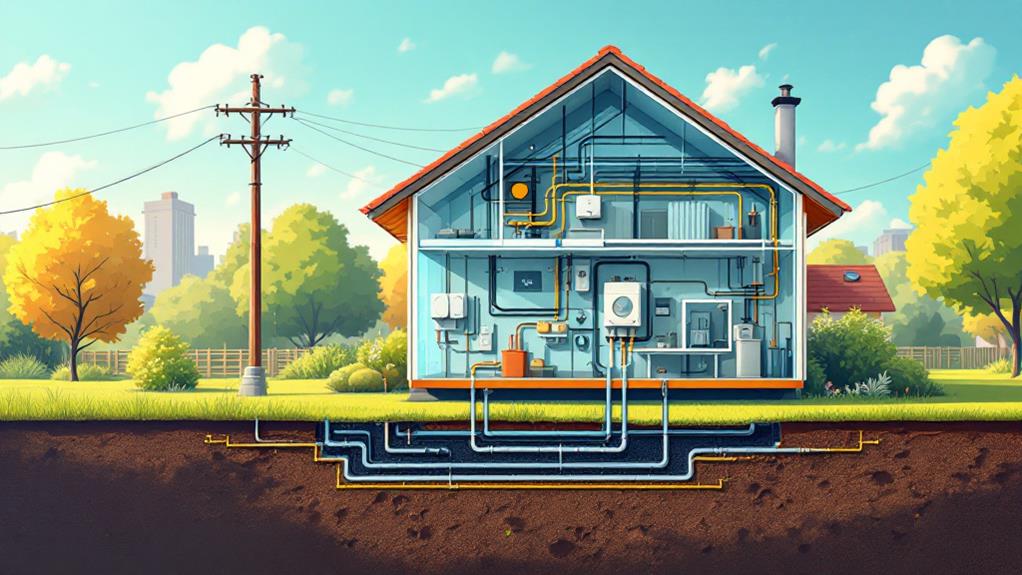

Now that electricity has navigated through the distribution network, it's ready to enter your home through the home electrical connection. This connection is fundamental for guaranteeing electricity is safely and efficiently distributed throughout your living space. Initially, electricity enters your home via a service drop, connecting to the meter that measures usage. From there, it flows into the main service panel, or breaker box, which houses circuit breakers that protect against overloads and short circuits, guaranteeing electrical safety.
To make certain your home wiring is efficient and up-to-date, consider these key components:
- Wiring Diagrams: Integral for planning and troubleshooting, they illustrate the intricate web of wires and connections.
- Load Calculation: Helps determine the total electrical demand of your home to prevent overloads and improve energy efficiency.
- Electrical Codes: Adherence to these regulations guarantees safety and reliability in your electrical system.
Smart homes often incorporate advanced technologies for increased energy efficiency and monitoring. By understanding and following these principles, you'll maintain a safe, efficient, and compliant electrical system. Remember, proper installation and maintenance of your home electrical connection are critical for peak performance and safety.