The Greatest Medical Breakthroughs in History: Milestones in Medicine

Medical breakthroughs have revolutionized healthcare throughout history. You've likely benefited from antibiotics, vaccines, and medical imaging techniques like X-rays and MRIs. Anesthesia has made surgeries safer and less painful, while organ transplantation has given countless people a second chance at life. The discovery of DNA's structure paved the way for gene therapy and personalized medicine. Stem cell research offers hope for regenerative treatments, and artificial intelligence is enhancing diagnostics and treatment plans. These milestones have dramatically improved human health and longevity, but they're just the tip of the iceberg in medicine's fascinating expedition.
The Discovery of Antibiotics
In the midst of the 20th century, antibiotics burst onto the medical scene, revolutionizing the treatment of bacterial infections. You might know Alexander Fleming as the accidental uncover of penicillin in 1928, but it wasn't until the 1940s that antibiotics became widely available. These wonder drugs quickly altered medicine, saving countless lives from previously deadly infections.
Antibiotics work by either killing bacteria or preventing their growth. They've become essential in treating a wide range of conditions, from strep throat to pneumonia. However, their widespread use has led to new challenges. Antibiotic resistance challenges have emerged as bacteria evolve to withstand these drugs, making some infections increasingly difficult to treat.
Another concern is antibiotics and microbiome disruption. When you take antibiotics, they don't just target harmful bacteria; they can also affect the beneficial microbes in your gut. This disruption can lead to digestive issues and potentially contribute to other health problems. As a result, researchers are now focusing on developing more targeted antibiotics and exploring alternative treatments to combat bacterial infections while minimizing these side effects.
Vaccination and Disease Eradication
Leveraging the power of the human immune system, vaccination stands as one of the most significant medical breakthroughs in history. You've likely benefited from this revolutionary approach to disease prevention, which has saved countless lives since its inception. Vaccines work by introducing a weakened or inactivated form of a pathogen into your body, stimulating your immune system to create antibodies without causing the actual disease.
The concept of vaccination dates back to 1796 when Edward Jenner developed the first vaccine against smallpox. Since then, we've made exceptional strides in eradicating deadly diseases. The most notable success is the global elimination of smallpox in 1980, a feat achieved through widespread vaccination campaigns.
Vaccines don't just protect individuals; they create herd immunity, shielding entire communities from outbreaks. This collective protection is pivotal for those who can't be vaccinated due to medical reasons. Today, you have access to vaccines for numerous diseases, including polio, measles, and influenza. Ongoing research continues to expand the reach of vaccination, targeting diseases like malaria and HIV, promising a future where more devastating illnesses can be prevented or eradicated entirely.
X-rays and Medical Imaging
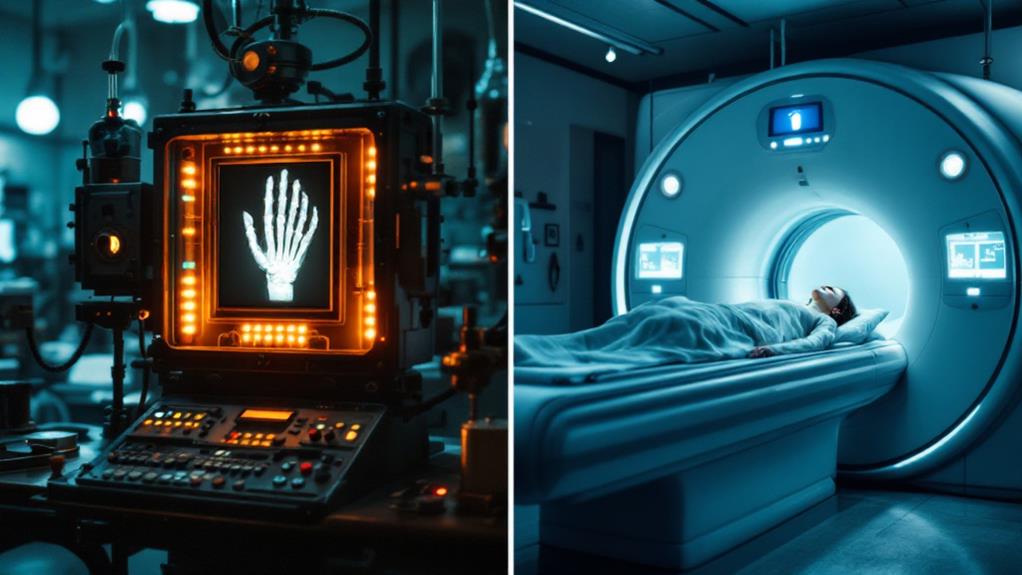
Peering beneath the surface of the human body, X-rays revolutionized medical diagnosis and treatment. When Wilhelm Roentgen uncovered X-rays in 1895, he opened up a new world of possibilities for doctors. You can now see inside the body without invasive procedures, allowing for quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
As technology advanced, so did medical imaging. You've likely experienced various forms of imaging techniques, each offering unique observations into your body's inner workings:
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans, creating detailed cross-sectional images
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), using powerful magnets to visualize soft tissues
- Ultrasound, employing sound waves to generate real-time images
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET), revealing metabolic processes within the body
These innovations have transformed healthcare, enabling early detection of diseases and guiding surgical procedures. With the advent of digital imaging and advanced image processing techniques, doctors can now manipulate and enhance images for better interpretation. However, the use of X-rays and other radiation-based imaging methods has also led to increased awareness of radiation exposure risks. As a result, radiation safety protocols have been developed to protect both patients and healthcare workers while still reaping the benefits of these priceless diagnostic tools.
Anesthesia in Surgery
Pain-free surgery was once an impossible dream, but anesthesia changed all that. You can thank Crawford Long and William T.G. Morton for pioneering the use of ether as an anesthetic in the 1840s. This breakthrough revolutionized surgical procedures, allowing doctors to perform more complex operations without patients experiencing excruciating pain.
As anesthesia techniques evolved, so did pain management techniques and surgical safety protocols. Today, you'll find a team of anesthesiologists and nurses monitoring your vital signs throughout surgery, ensuring you remain unconscious and pain-free. They'll adjust the dosage of anesthetics and use various drugs to control your blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing.
Modern anesthesia isn't just about keeping you asleep during surgery. It's a sophisticated blend of medications customized to your specific needs, medical history, and the type of procedure you're undergoing. From general anesthesia that renders you completely unconscious to regional anesthesia that numbs specific areas of your body, these techniques have made even the most invasive surgeries more bearable and safer than ever before.
Organ Transplantation
How would you feel if you could give someone a second chance at life? That's exactly what organ transplantation has made possible. Since the first successful kidney transplant in 1954, this medical breakthrough has saved countless lives and transformed healthcare.
Organ transplantation has evolved dramatically over the years. Today, you can witness:
- Heart transplants that give patients a new lease on life
- Liver transplants restoring health to those with failing organs
- Lung transplants allowing recipients to breathe freely again
- Cornea transplants restoring sight to the visually impaired
The field continues to advance with living donor transplants, where healthy individuals can donate organs like kidneys or partial livers to those in need. This has considerably reduced waiting times and improved outcomes for recipients.
Researchers are also making strides in artificial organ development. You might soon see bioengineered organs or 3D-printed tissues becoming viable alternatives to donor organs. These innovations could potentially eliminate organ shortages and rejection issues, making transplantation even more accessible and successful.
As organ transplantation techniques improve, you're witnessing a medical miracle that's giving hope to millions worldwide.
DNA Structure and Gene Therapy
The unraveling of DNA's double helix structure in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick revolutionized our understanding of genetics and laid the foundation for gene therapy. This revelation paved the way for advancements in genetic engineering and gene sequencing, allowing scientists to manipulate and study genes with unparalleled precision.
Gene therapy, a direct result of our understanding of DNA, offers hope for treating genetic disorders by introducing functional genes into patients' cells. You'll find that this approach has shown promise in addressing conditions like cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, and certain types of cancer. As gene sequencing techniques have improved, we've gained the ability to identify genetic markers for diseases and personalize treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup.
The Human Genome Project, completed in 2003, marked a significant milestone in DNA research. It provided a complete map of human genes, accelerating our understanding of genetic diseases and opening new avenues for targeted therapies. Today, CRISPR gene-editing technology is pushing the boundaries of genetic engineering, offering potential cures for previously untreatable conditions and raising ethical questions about the future of human genetic modification.
Stem Cell Research

Countless medical breakthroughs have emerged from stem cell research, revolutionizing our approach to treating previously incurable diseases. You've likely heard about stem cells' potential to repair damaged tissues and organs, but their impact extends far beyond that. Stem cell research has paved the way for regenerative medicine, offering hope for patients with conditions like heart disease, Parkinson's, and spinal cord injuries.
In tissue engineering, scientists are now able to cultivate complex structures, such as:
- Miniature organs called organoids
- Artificial skin for burn victims
- Lab-grown cartilage for joint repairs
- Blood vessels for cardiovascular treatments
You'll find that stem cell therapies are already being used to treat blood disorders and certain cancers. As research progresses, you can expect to see more applications in personalized medicine, drug development, and even 3D-printed organs. The field continues to evolve rapidly, with new findings constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible. While ethical concerns have sparked debates, the potential benefits of stem cell research in saving lives and improving quality of life are undeniable.
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing healthcare, altering how you receive medical care and how doctors diagnose and treat diseases. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of medical data, including patient records, research papers, and clinical trials, to provide more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. These systems can detect patterns and anomalies that human doctors might miss, potentially saving lives through early detection of diseases like cancer.
Predictive analytics, a key application of AI in healthcare, helps identify patients at risk of developing certain conditions. This allows for preventive measures to be taken before symptoms appear. AI also enhances telemedicine, enabling remote consultations and monitoring. You can now receive expert medical advice from the comfort of your home, with AI algorithms assisting doctors in interpreting your symptoms and medical history.
AI is revamping medical imaging, too. It can quickly analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, helping radiologists spot potential issues more efficiently. As AI continues to advance, you'll likely see even more personalized and efficient healthcare, with robots assisting in surgeries and AI-powered devices monitoring your health in real-time.