Muscles are an essential part of our body, allowing us to move, lift, and perform various physical activities. However, they are also vulnerable to inflammation, which can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Muscle inflammation, also known as myositis, can occur for various reasons, ranging from overuse and injury to infections and autoimmune disorders. Understanding what causes muscle inflammation is crucial for preventing and treating this common condition. In this article, learn about the various factors contributing to muscle inflammation and its treatments.
Causes of Muscle Inflammation
Muscle inflammation, also known as myositis, can be caused by a variety of factors. Some common causes of muscle inflammation include:
Overuse or injury
When muscles are overworked or subjected to repetitive strain, they can become inflamed. This is common among athletes who engage in intense physical activity. Vigorous exercise can lead to muscle pain, swelling, and weakness for hours or days after a workout or a game. Inflammation contributes to these symptoms, which makes it a form of myositis. Inflammation symptoms nearly always resolve completely after rest and recovery.
Infection
Certain viral and bacterial infections can cause muscle inflammation. Viral infections are the types of infections that most commonly cause myositis. Rarely fungi, bacteria, and other organisms can cause myositis as well. Viruses or bacteria may invade the muscle tissue directly or release substances that cause damage to muscle fibers. For example, the common cold and flu viruses can cause myositis, as can the bacterium that causes Lyme disease. Other infectious diseases like HIV, hepatitis B, and C, and influenza may also cause muscle inflammation.
Medications
Some medications can cause temporary muscle inflammation as a side effect. Because the inflammation in the muscles is often not identified, the muscle problem may be considered a myopathy rather than myositis. Drugs that cause myositis or myopathy include:
- Statins
- Cocaine
- Colchicine
- Alpha-interferon
- Plaquenil (hydroxychloroquine)
- Alcohol
Myopathy can start right after starting a drug or may occur after taking the medication for months or years. Sometimes, it’s caused by an interaction between two different medications. But luckily, it’s rare to develop severe myositis due to medications.
Genetic factors
Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing myositis or other inflammatory conditions. Several different genes have been identified as playing a role in the development of myositis, and the specific genes involved can depend on the type of myositis.
For example, in familial inclusion body myositis (IBM), which is a rare form of myositis that tends to run in families, several genes have been identified as potential contributors to the condition. Among others, mutations in the GNE, VCP, and MYH2 genes have been associated with IBM.
Similarly, polymyositis and dermatomyositis have also been linked to specific genetic factors. For example, the HLA-DR3 and HLA-DRw52 genes have been associated with an increased risk of developing these conditions.
Autoimmune disorders
In some cases, the body’s immune system may mistakenly attack muscle tissue, leading to inflammation. This is known as autoimmune myositis and can be associated with conditions such as lupus, scleroderma, and rheumatoid arthritis. These inflammatory conditions tend to cause milder forms of myositis.
Meanwhile, inflammatory types of myositis cause potentially severe inflammation of the muscles, including polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and inclusion body myositis. These are autoimmune conditions in which the body attacks its own tissues. Inflammatory conditions are often the most serious causes of myositis, requiring long-term treatment.
Other medical conditions
Besides autoimmune disorders, other medical conditions can also cause muscle inflammation. These conditions include hypothyroidism, diabetes, and vasculitis.
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is a condition characterized by the breakdown of muscle fibers that release their contents, including a protein called myoglobin, into the bloodstream. When this happens, the kidneys may become overwhelmed trying to filter out these substances, leading to kidney damage or even failure. Muscle pain, swelling, and weakness are symptoms of this condition. Urine may also become dark brown or red in color.
Symptoms of Myositis
The symptoms of myositis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, and it usually develops gradually. However, some common symptoms of myositis include:
- Muscle weakness – This is one of the major symptoms of myositis and may occur in the arms, legs, or trunk muscles.
- Fatigue – Myositis can cause significant fatigue and weakness, making it challenging to perform routine activities.
- Difficulty lifting arms or moving limbs – As the muscles become inflamed, a person with myositis can feel difficulty moving the limbs and even lifting the arms.
- Muscle pain – Some people with myositis have muscle pain, but many do not.
- Difficulty swallowing – Myositis can affect the muscles involved in swallowing, making it difficult to eat or drink.
Polymyositis and dermatomyositis often come with periods of worsening symptoms called flares. It tends to cause weakness that gets worse slowly over weeks or months, which affects the large muscle groups, including the neck, shoulders, back, and hips. Muscles on both sides are typically affected. The weakness. Besides the symptoms mentioned above, a person with inflammatory myositis may also experience the following:
- Rash – Rashes associated with dermatomyositis are patchy, purple, or red and can be found on the face, elbows, eyelids, knees, toes, back, or chest. Rashes can appear before, after, or during symptoms of muscle weakness.
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- Thickening of the skin on the hands
People with myositis caused by a virus typically have symptoms of viral infection, such as:
- Fever
- Runny nose
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
Health Effects of Myositis
Inflammation of the muscles not only brings discomfort but can also have a range of health effects on the person experiencing it. Since myositis weakens the muscles, it makes it difficult for a person to perform ordinary, routine activities. In some cases, it can lead to significant disability and difficulty performing activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, and grooming.
In severe cases of myositis, weakness in the muscles involved in breathing can lead to respiratory problems, such as shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, or respiratory failure.
Weakness of the throat muscles can cause trouble swallowing, called dysphagia. About one-third of people with myositis experience this issue. It makes it less enjoyable to eat and drink, which may cause significant weight loss as well.
If the heart muscle is inflamed, the condition is called myocarditis, and it can lead to tissue scarring and poor heart function. Meanwhile, if the lung tissue is scarred, it causes breathing problems. About 30-40 percent of people with myositis have some form of lung disease.
In dermatomyositis, the condition can cause a rash on the face, neck, chest, back, and hands. The rash may appear red or purple, and the skin may feel rough or scaly.
Myositis can also cause problems in the joints, as it brings about pain and swelling, particularly in the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles.
This condition doesn’t cause cancer, but people with chronic myositis – especially dermatomyositis – are more likely to develop cancer. Experts believe that an improperly working immune system plays a big role.
As you can imagine, almost everything else can be affected when the muscles are weakened. People living with this chronic condition can lead a challenging life, which can make them develop depression and anxiety.
Treatment of Myositis
The treatment of myositis depends on the type and severity of the condition, as well as the underlying cause. Some common treatments for myositis include:
Medications
Corticosteroids are often used to reduce inflammation and improve muscle strength. These are usually given through injection.
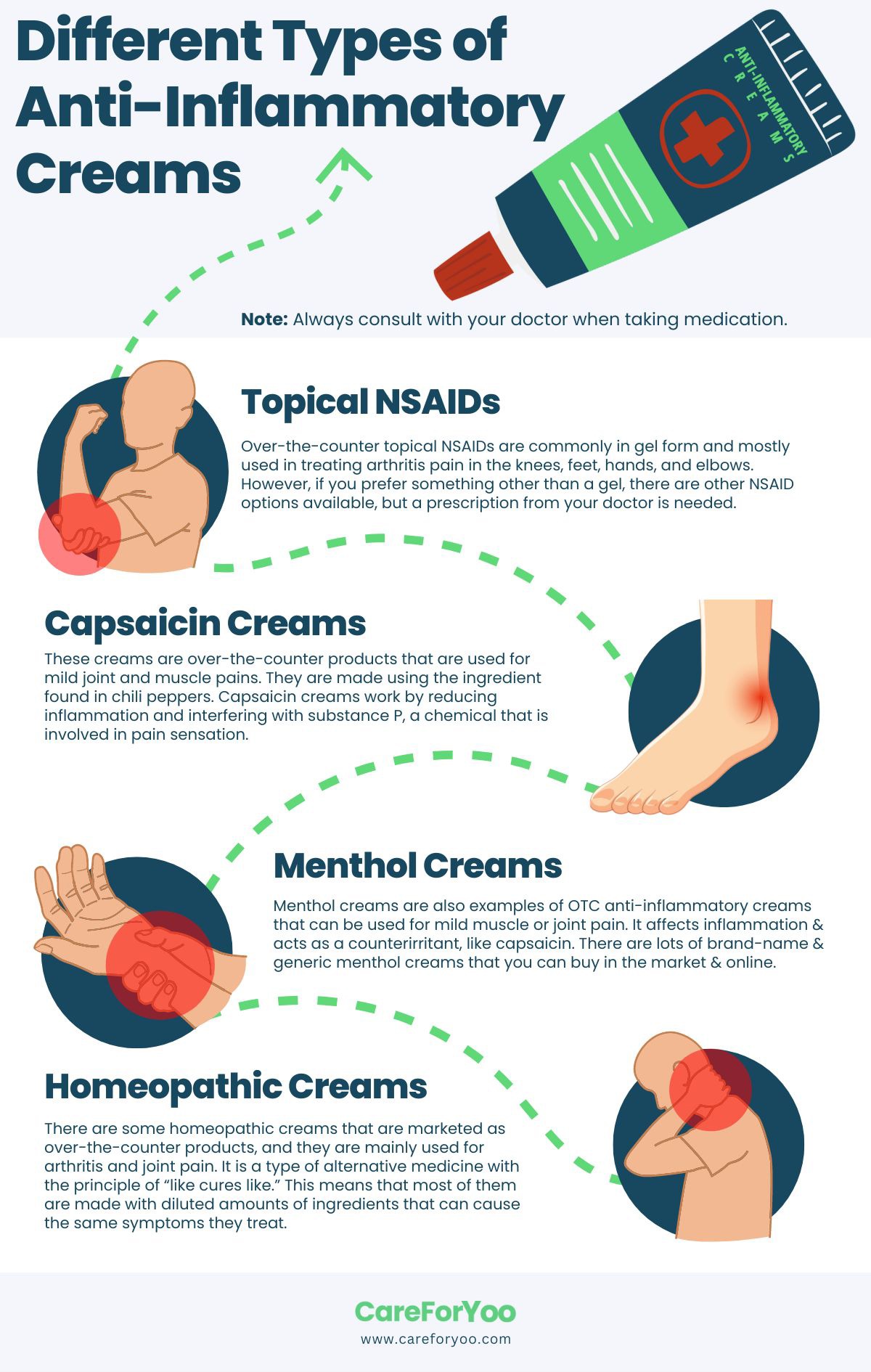
Immunosuppressive drugs are the next treatment option if corticosteroids do not relieve the symptoms. Inflammatory conditions that cause myositis may require treatment with drugs that suppress the immune system, including prednisone, methotrexate, and azathioprine. Anti-inflammatory creams may also help alleviate symptoms.
If the muscle inflammation is due to infection caused by a virus, no specific medication is necessary. But if bacteria cause it, it requires antibiotics to prevent the life-threatening spread of the infection.
Immunosuppressive medications may also be prescribed to suppress the immune system and prevent further damage to the muscles.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can help maintain muscle strength and flexibility, improve range of motion, and reduce pain and stiffness. It can also help prevent muscle weakness and atrophy.
Exercise
Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, and cycling, can help improve muscle strength and function without causing further damage.
Rest
Rest is essential for allowing the muscles to heal and recover from inflammation and injury. If the myositis is caused by injury or overuse, the proper thing to do is to rest the body.
Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy can help individuals with myositis learn new ways to perform everyday tasks and activities, reducing the strain on the affected muscles.
Surgery
In rare cases, surgery may be required to remove damaged or inflamed tissue or to address complications, such as difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Self-Care Tips for Myositis
If you are living with myositis – or know someone who does – there are several tips you can follow to manage the condition. Here are some self-care strategies that may be helpful:
Adopt an anti-inflammatory diet
There’s no diet that can cure myositis, but adopting an anti-inflammatory diet may help. This includes eating plenty of fruits and vegetables, with an aim to eat a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables every day. Choose to eat healthy fats, like fatty fish, nuts, and seeds. Avoid processed foods and limit your intake of refined carbohydrates.
Follow your treatment plan
Following your healthcare professional’s treatment plan, including taking medications as prescribed, attending appointments, and following any recommended lifestyle changes, is essential. Follow your physical therapist’s instructions for regular exercise to keep muscles strong and flexible.
Rest and conserve energy
Myositis can cause fatigue and weakness, so it is important to rest when needed and conserve your energy throughout the day. You will need to take frequent breaks, pace yourself, and prioritize tasks.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle
Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help manage myositis symptoms and promote overall health. Even if it can be a little difficult to swallow due to your condition, see to it that you are taking at least three meals.
Manage stress
Stress can exacerbate myositis symptoms, so finding ways to manage stress is essential. Manage your stress levels to help boost the immune system and mood. Mind-body techniques like meditation or yoga, seeking support from friends and family, or working with a mental health professional can help you de-stress.
Protect your skin and avoid infections
Dermatomyositis can cause sensitivity to sunlight, so it is important to wear protective clothing and sunscreen when outdoors. Avoid sun exposure during peak hours. Avoiding infections by washing your hands frequently, avoiding sick individuals, and getting recommended vaccinations are also essential.
Work with a healthcare team
Manage your condition with a healthcare team. You may need the help of your primary care physician, a rheumatologist, a physical therapist, and an occupational therapist. You may not need to get all of them, but these professionals can best help manage your myositis and address any complications or concerns that may arise.