What Is an Electric Vehicle? A Beginner’s Guide to EVs

Electric vehicles (EVs) are changing the driving landscape with their groundbreaking battery technology and reduced environmental impact. You'll find three main types: Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) that run solely on battery power, Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) that combine batteries and gasoline, and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) which use gas engines alongside electric motors. EVs offer cost savings on fuel and maintenance, but the initial purchase price is higher. Efficient charging infrastructure is essential, with home and public charging options available. Uncover how EVs improve driving with instant torque and government incentives that make them more affordable.
Understanding Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) have become a crucial part of the modern transportation landscape, and understanding them is significant for anyone considering a switch from traditional gas-powered cars. At the heart of EVs lies cutting-edge battery technology, which differentiates them from conventional vehicles. These batteries, primarily lithium-ion, store and provide energy efficiently, ensuring you get the performance you expect. Advances in battery technology have led to longer ranges and faster charging times, making EVs more practical than ever.
The EV market is expanding rapidly, offering a wide array of options tailored to different needs and budgets. As you investigate this evolving market, you'll notice that manufacturers are committed to improving battery life and charging infrastructure. This commitment means that EVs are becoming more accessible and convenient. The growing EV market also means competitive pricing, which can make the shift smoother for you.
Types of Electric Vehicles
There are several types of electric vehicles available today, each catering to different preferences and needs. Understanding these can help you choose the right EV model for your lifestyle. Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) run entirely on battery technologies and need a strong charging infrastructure for convenient use. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) combine battery power with a gasoline engine, offering flexibility if charging stations aren't nearby. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) use the combustion engine more but still benefit from electric efficiency.
Market trends show a rise in BEVs due to government incentives and growing consumer preferences for eco-friendly options. Performance comparisons between different EV models highlight differences in range, speed, and efficiency, which are vital when deciding which type to buy. Maintenance tips for these vehicles also differ; generally, EVs require less upkeep than traditional cars.
Consider these key points when exploring types of electric vehicles:
- Battery technologies: Determine the range and efficiency.
- Charging infrastructure: Assess availability in your area.
- Government incentives: Check for financial benefits.
- Consumer preferences: Choose based on lifestyle needs.
- Performance comparisons: Evaluate speed, range, and cost.
How Electric Vehicles Work
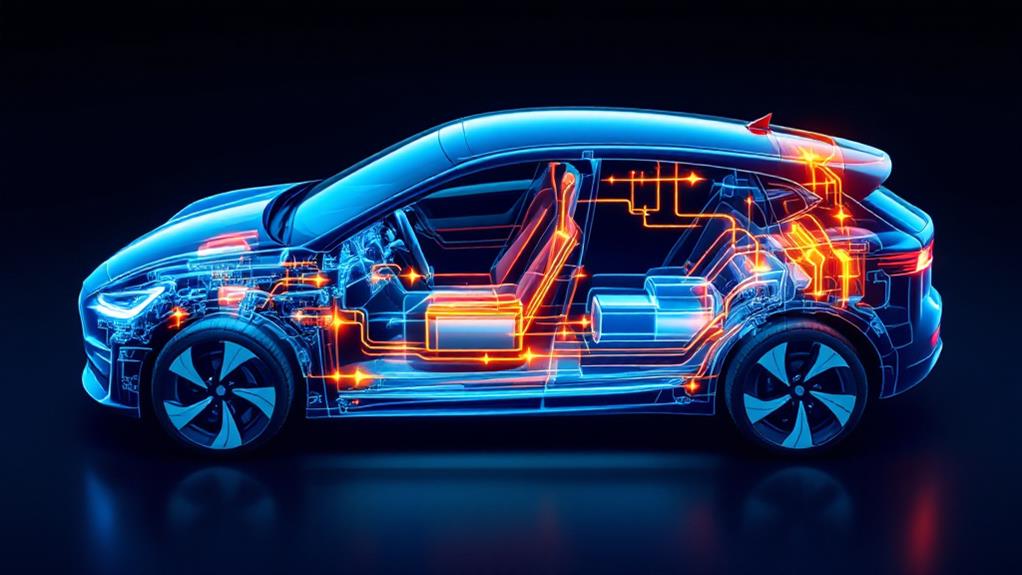

Understanding the mechanics of electric vehicles can demystify how they function and highlight their advantages. At the heart of every EV is advanced battery technology, which stores energy to power the car's electric motors. These motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, setting the vehicle in motion. Unlike conventional engines, electric motors offer a smoother driving experience with instant torque and quieter operation.
One key feature is regenerative braking, a system that recovers energy typically lost during braking. This energy is sent back to the battery, enhancing the vehicle range. With efficient use, you can travel longer distances without frequent stops.
The EV's efficiency extends to its maintenance requirements. Fewer moving parts mean less wear and tear, reducing service visits and costs. Additionally, the growing charging infrastructure makes it easier to keep your EV powered, although it is crucial to plan your routes around available stations.
Government incentives also play a role in making EVs attractive, as they can offset initial costs or provide tax benefits. By understanding these aspects, you can appreciate how EVs not only work but also why they're becoming a popular choice for modern drivers.
Charging an Electric Vehicle
Charging your electric vehicle (EV) is a straightforward process, but understanding the options available can improve your driving experience. You can charge your EV at home or utilize public charging stations. Home charging is convenient and allows you to plug in overnight, guaranteeing a fully charged vehicle by morning. Charging times may differ depending on the charging technology used, with Level 1 chargers being slower and Level 2 faster.
Public charging is ideal when you're on the go. Many charging networks offer fast charging options, drastically reducing charging times compared to home setups. Fast charging stations can charge your EV up to 80% in about 30 minutes, making them perfect for longer trips. However, charging costs can vary between home and public options, so it's wise to take into account your budget.
Charging safety is essential. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and confirm your home wiring is suitable for EV charging. When using public stations, keep an eye out for any damage to the equipment.
Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Home charging offers convenience and overnight charging.
- Public charging stations are widely available.
- Charging networks provide access to multiple stations.
- Fast charging saves time on the road.
- Charging costs and safety should be factored into your routine.
Environmental Impact of EVs

When you think about the environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs), it's clear they present a significant advantage over traditional gasoline-powered cars. EVs have lower lifecycle emissions, meaning from production to disposal, they generally emit fewer greenhouse gases. This is largely because they use electricity instead of burning fossil fuels. You can reduce emissions further by using renewable energy sources like solar or wind to charge your EV.
However, there's more to reflect on. The production of EV batteries, and the necessity for efficient battery recycling, can affect their overall environmental impact. Fortunately, advancements in recycling technology are helping to mitigate some of these concerns, making it easier to reuse valuable materials.
Charging infrastructure is another essential aspect. As more charging stations become available, it encourages the use of EVs, influencing consumer behavior towards greener choices. Urban planning plays a significant role here, as cities that prioritize charging facilities and integrate EVs into public transport systems can improve their sustainability efforts.
Ultimately, your personal choices as a consumer can drive demand for cleaner technology and better infrastructure, reinforcing the positive environmental impact of EVs.
Benefits of Driving an EV
Driving an electric vehicle (EV) offers a host of benefits that extend beyond just being environmentally friendly. You'll find that EVs can greatly reduce your total expenses. With lower fuel costs and fewer maintenance requirements—thanks to fewer moving parts—you'll enjoy considerable cost savings over time. The driving experience is also improved with instant torque and smoother acceleration, making every trip more enjoyable.
Government incentives can make your EV purchase even more appealing. Tax credits and rebates can offset the initial cost, providing immediate financial relief. Plus, as technology advancements continue, you'll see enhancements in battery life and efficiency, reducing concerns like range anxiety and making EVs more practical for longer trips.
Consider the following benefits:
- Cost Savings: Reduced fuel and maintenance expenses can lead to notable financial advantages.
- Improved Driving Experience: Instant torque and smooth acceleration make for a more enjoyable ride.
- Government Incentives: Tax credits and rebates can lower the initial cost of your EV.
- Advancing Technology: Advances in battery life and efficiency reduce range anxiety.
- Resale Value: As EVs gain popularity, their resale value could remain strong.
Challenges and Considerations

Maneuvering the world of electric vehicles comes with its own set of challenges that are significant to reflect upon. Infrastructure challenges can be intimidating, especially if you're in an area with limited charging stations. This scarcity can lead to range anxiety, where you worry about your vehicle running out of power before reaching a charging point. It's essential to plan your routes and charging stops effectively to avoid this stress.
Cost factors also play a big role. Although the initial purchase price of an electric vehicle can be higher than traditional cars, government incentives can help offset some of these costs. However, long-term savings on fuel and maintenance should also be included in your decision-making process.
Maintenance issues are generally fewer in electric vehicles, but they're not entirely absent. Battery disposal is another significant aspect to reflect upon. Proper disposal and recycling of EV batteries are vital for environmental sustainability.
Lastly, consumer adoption is gradually increasing, but it still faces resistance due to the unfamiliarity and perceived inconveniences. As more people switch to electric vehicles, you'll likely see improvements in infrastructure and technology, making the shift easier for future adopters.