All of us live in a world that can sustain life. Our planet is capable of supporting not just human life, but as well as animals, plants, and other organisms. It did a great job of sustaining lifeforms for billions of years. As time goes on, lifeforms on earth continue to co-exist with each other, wherein humans are considered as the dominant species and is at the top of the food chain.
The existence of humans, animals, and plants holds several mysteries, which caught the interest of various people around the globe in different generations. These people dedicated a part of their lives to studying these lifeforms and contributed to the advancement of science. The study of living organisms sparked the creation of the branch of science called biology.
We might be familiar with the definition of biology since it is a part of our education, along with other branches of science. In this article, we are going to look into the meaning of biology, and mainly – what is its history?
What is biology?
Biology is a field of natural science that focuses on the study of life and living organisms. This science includes several other branches, which study more specific subjects, such as botany, zoology, ecology, entomology, and ichthyology. This field itself is diverse and covers various topics, which relate to the properties of life.
In biology, it states that the cell is the basic unit of life, and every living organism here on earth is composed of cells. It includes animals, plants, and other living organisms. Another fact for all living things is they require energy, which creates a cycle between lifeforms and the environment.
What is the origin of biology?
Biology came a long way throughout history to reach a well-developed stage that is capable of defining certain phenomena about life. We can trace back the incredible history of biology to ancient times when natural philosophers were present in different countries around the globe. Natural philosophy focuses on the study of nature, although ancient philosophers often relate these phenomena to magic or mythology. Despite not having any concrete scientific evidence, natural philosophy was a significant milestone in the development of science since it sparked interest and curiosity for many scientists. Furthermore, this study originated from ancient China, India, Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece, which causes it to have various cultural differences during its development stage.
Among all the known origins of biology, experts often consider Greece as to where it originated its modern practice. This speculation is primarily because of the Greek philosopher Aristotle, who made a massive influence on the advancement of biology in the Western Countries. He was the first person to study the probable cause and effect of nature, mainly in animals. His work made a significant impact on the study of biology since he based them on scientific observations and experimentations, which helped produce great results.
Aristotle pioneered the study of biology and made the framework for zoology – which is a branch of science specializing in the study of animals. He compiled his learnings into a written text called ‘History of Animals,’ which shows the pioneering work of zoology. He created the text based on his observations of animals in nature, identifying their similarities and differences, and dividing them into groups based on these features. The perfect example of this is birds, which mostly have beaks, wings, and feathers – creating a common factor for each species.
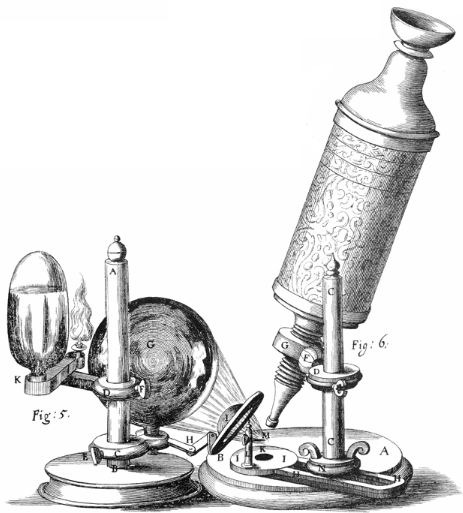
Over the years, the development of biology advanced rapidly, especially during the 17th century when the Dutch businessman and scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek made his contribution to the study of science. He contributed remarkable discoveries in biology with the help of the early microscopes, which exposed the diversity of microscopic life. Experts consider him as the pioneer of microscopy and the founder of microbiology. His work gained him recognition in the field of biology, which earned him the title ‘Father of Microbiology.’
During this period, an English scientist named Robert Hooke discovered the existence of cells, which led to further studies regarding the more complex structure of life. Fast forward to the 19th century when various biologists contributed to the study of cells, pointing out its importance. This sparked the concept of cell theory, which is developed by Robert Remak and Rudolf Virchow.
Today, scientists all around the world continue to study the mysteries of biology. Each year, numerous discoveries are made to further develop our modern science.