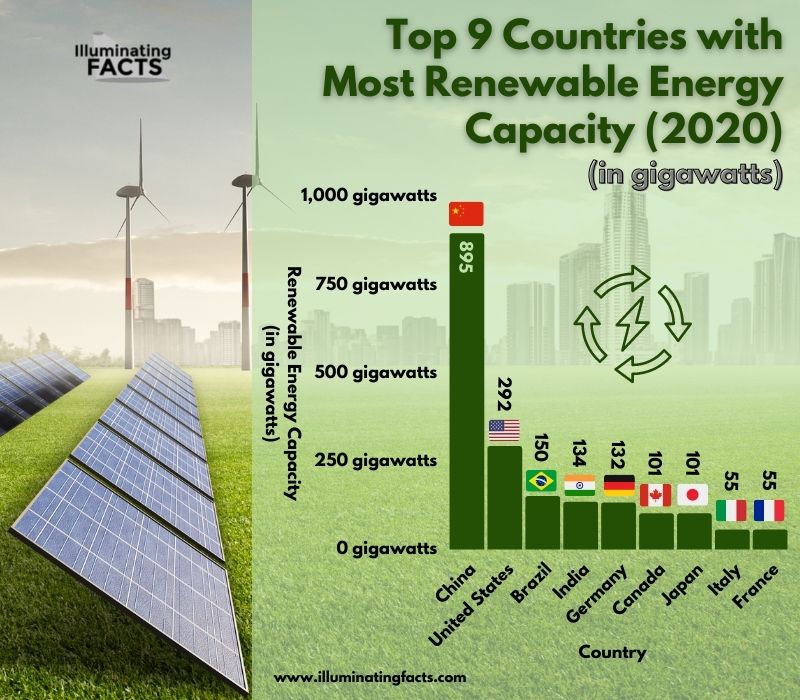
In the wake of an alarming climate crisis in recent times, the need to move towards renewable energy is more dire than ever before. Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are constantly being replenished as part of natural processes on Earth. Check out this graph from IlluminatingFacts.com ranking the top countries for renewable energy production:
Some examples of sources converted to power are solar energy, tidal energy, and wind energy. These come from the heat of the sun, the force of tides in the ocean or seas, and the force of the wind, respectively. It is essential to understand how intricately these naturally occurring phenomena are manipulated to produce one of the most important facilities for the world in a more environment-friendly way.
Let us take a deep dive into how wind is converted into electrical power across the world through advancements in technology.
Wind
Scientists have classified wind as a form of solar energy. They do so as they have found that wind occurs, among other things, due to changes in the atmosphere caused by the sun. When the sun heats the atmosphere unevenly, the wind is produced. Moreover, the variations in the surface of the Earth, its terrain, and the rotation of the Earth also play a role in the formation of wind.
The flow of the wind varies significantly across the world and in different topographies. These flow and air pressure variances are studied, closely monitored, and used to benefit the world by producing wind energy. Wind turbines are used to carry out the production of wind energy.
Wind Turbines
Similar to the use of solar panels to convert solar energy into power, wind turbines are used to convert the energy from the wind into power. The wind turbines have several components that have their own functions, but they work in harmony.
Foundation
The foundation is the base that the turbine stands on and is hence weighted. It cannot be seen irrespective of which type of turbine we look at. It is either covered with soil or water.
Tower
The tower is a metal rod that vertically protrudes from the foundation. It is approximately 75-110 meters tall. The height is determined based on the location and size of the turbine.
Rotor
The part of the turbine that moves with the wind is called the rotor. The blades and the hub are fixed to the rotor. The blades are very light-weighted.
Hub
The hub is the central part to which the blades are attached. It is responsible for providing momentum for the easy movement of blades.
Nacelle
The nacelle is placed at the top of the tower and consists of essential components that work in the mechanism of the turbine, mainly the gearbox. The gearbox manages the speed of the generator.
Generator
The generator is the component that does the final work. It converts kinetic energy into electrical energy. It needs a specific speed to move at so it can do its job.
There are two types of wind turbines: horizontal-axis and vertical-axis turbine. The horizontal axis one is the most commonly known, with three wings. Their blades need to face the wind to work. On the other hand, the vertical axis turbine is the one that comes in a shape that looks like an eggbeater. These are designed to ensure that the direction of the wind does not impact their performance. They are omnidirectional and hence, arguably, more efficient in producing electricity.
The science behind wind converted into power?
Power plants are set up to produce electricity through different sources; in the case of wind energy, it is called a wind farm. To learn more about the evolution of power plants through time, click here.
A wind farm houses several wind turbines. The wind energy from the groups is taken all together and then transmitted forward to houses or industries. But how does the conversion happen?
As wind flows, it moves the rotor blades. Due to a difference in the air pressure on both sides of the blade, the rotor starts to move. The spinning of the rotor sends energy to the generator through a shaft and gearbox. The gearbox further increases the speed. The generator is connected and begins to generate electricity.
The mechanics of the windmill stay the same irrespective of where it is placed.
Types of wind energy
Mainly two types of wind energy exist. Their type is determined based on where they are installed: on land or off land.
- On-shore wind energy
As the name suggests, energy is produced by wind turbines that are installed on land. Mostly they are on a wind farm, along with others.
- Off-shore wind energy
This wind energy is produced from wind turbines that are placed in water bodies. They are massive as they have to catch the strong winds that are found in oceans. More energy is produced from these as compared to the onshore turbines. The foundation for these turbines is installed on the seabed.
Cost of wind energy
Wind energy is cheaper than other forms of energy. Houses located in the countryside allow smaller wind turbines to be installed to power these houses. These do require a heavy initial investment. However, later on, no other costs are incurred apart from basic maintenance and repair. The cherry on top is that hefty bills previously being paid for power will be cut down.
Why is wind energy said to be the best option?
The case in favor of wind energy is pretty strong since the pros heavily outweigh the cons. Here are a few reasons why wind energy production has rapidly increased compared to other non-renewable sources of energy.
Clean
No emissions are created as a result of energy production by wind, making it pollution-free. Wind farms do not require vast construction, and instead, the natural terrain of the area is maintained. Moreover, no fuels are used to convert energy like it is done in other sources like hydropower and biomass.
Wind energy does not contribute to the destruction of land or the environment. Since there are no emissions, human and animal lives are not put at risk of damage through harmful gases. The carbon footprint is extremely low.
Cost-effective and affordable
Wind energy has been found to be the most inexpensive source of electricity per kilowatt. A fixed price is agreed upon already, and long-term agreements are signed. This makes it easier to pay over a few years. The cost is minimum too, which further makes it cheaper.
Sustainable
As discussed previously, wind is a form of solar energy. The sun is abundant and forever, and as a result, so is wind. The source of wind energy cannot deplete, which makes this sustainable and reliable.
Job creation and revenue
The certainty of energy makes the return on investment higher and the risk lower. More people are willing to spend money on this, which further creates revenue for the country and jobs for its people. Not to mention, these jobs are GREEN!
Conclusion
This technologically advanced era will not only boost further advancements made in the field but will also contribute to further research on renewable sources of energy. Enhancing and polishing knowledge on renewable energy sources is a big step towards a healthier environment of the world.
It’s fair to say that the ins and outs of converting wind energy to power have been briefed over up until now. Following that trend of wind energy, try to learn all about windmills to further enhance your knowledge on the topic.